Sustainability has become a significant focus in residential construction as more people seek eco-friendly homes. Green building certifications help ensure that residential projects meet certain environmental standards. This article covers the main certification agencies, regulations, and criteria for green building certification in residential projects.
General Criteria for Green Building Certification
Sustainable Site Development
Sustainable site development involves careful site selection and planning to minimize environmental impact. This includes choosing locations with minimal ecological disruption, ensuring proximity to public transport, and preserving natural topography. Landscaping and ecology considerations, such as using native plants, green roofs, and urban agriculture, also play a crucial role.
Water Efficiency
Water efficiency is a key criterion for green building certification. Water conservation practices, such as rainwater harvesting and greywater recycling, are essential to reduce water usage. Additionally, using efficient fixtures and fittings, such as low-flow faucets and dual-flush toilets, helps minimize water wastage in residential buildings.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency involves optimizing building design to reduce energy consumption. This includes building orientation to maximize natural lighting and ventilation, using energy-efficient appliances and systems, and integrating renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines. These practices contribute to lower energy bills and reduced environmental impact.
Materials and Resources
Sustainable building materials are crucial for green building certification. This includes using recycled, locally sourced, and non-toxic materials in construction. Effective waste management practices, such as reducing construction waste and implementing recycling programs, are also important to minimize the environmental footprint of residential projects.
Indoor Environmental Quality
Indoor environmental quality focuses on maintaining healthy and comfortable living conditions. This includes ensuring good air quality through the use of low-VOC materials and effective ventilation systems. Lighting and acoustics are also important, with strategies for natural daylighting and noise control enhancing the overall living environment.
Innovation and Design
Innovation and design in green building involve integrating advanced technologies and practices to improve sustainability. This includes implementing smart home technologies, advanced energy management systems, and promoting sustainability education to encourage occupant awareness and participation in sustainable practices.
General Certification Process for Green Building Certification
Pre-certification Stage
The pre-certification stage involves initial planning to understand the certification requirements and set sustainability goals for the project. This stage also includes registering the project with the chosen certification body, laying the groundwork for the certification process.
Design and Construction Stage
During the design and construction stage, necessary documentation is gathered and submitted to demonstrate compliance with green building standards. This stage also involves integrating sustainable practices throughout the design and construction phases to ensure the project meets the required criteria.
Final Certification Stage
In the final certification stage, the project undergoes a third-party evaluation to verify compliance with the certification criteria. Based on performance, the project is awarded a certification level, such as Certified, Silver, Gold, or Platinum, recognizing its adherence to green building standards.
Types of Residential Buildings Eligible for Certification
Green building certifications can apply to various types of residential buildings, including single-family homes, multi-family homes, and mixed-use residential buildings. Single-family homes, such as detached houses and villas, can achieve certification by incorporating sustainable practices in their design and construction. Multi-family homes, including apartments, condominiums, and housing societies, can also be certified by following green building standards. Mixed-use residential buildings, which combine residential and commercial spaces, can achieve certification by integrating sustainable practices across both functions.
Also learn about Apartment Plan – Factors for design of residential apartment
Get your checklists for Green Building Regulations and Certifications

Overview of Certification Agencies
Indian Green Building Council (IGBC)
The Indian Green Building Council (IGBC), established by the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), promotes sustainable building practices. IGBC offers a specific certification for residential projects called IGBC Green Residential Societies. This certification covers various types of residential buildings and focuses on areas such as energy efficiency, water conservation, and sustainable materials. Following IGBC guidelines helps residential projects reduce their environmental impact and improve residents’ quality of life.
Types of Residential Buildings Covered:
- Individual Homes: Detached houses and villas.
- Multi-dwelling Units: Apartments, condominiums, and housing societies.
- Townships: Large residential developments that may include mixed-use areas.
Focus Areas:
- Site Selection and Planning: Emphasis on eco-friendly site choices, density, and access to amenities.
- Water Efficiency: Promotes water-saving fixtures and rainwater harvesting.
- Energy Efficiency: Advocates for energy-saving design and renewable energy use.
- Materials and Resources: Supports the use of sustainable building materials and waste reduction.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Ensures clean indoor air and natural ventilation.
- Innovation and Design Process: Encourages innovative designs and educates on sustainable practices.
Certification Process:
- Pre-certification Stage
- Project Registration: The first step involves registering the project with IGBC to receive a project ID and access to the necessary resources.
- Initial Assessment: Understanding the specific requirements and preparing the project to meet IGBC criteria.
- Design and Construction Stage
- Documentation: Compiling and submitting documents that demonstrate compliance with IGBC’s criteria.
- Implementation: Integrating green building practices into the project’s design and construction phases to ensure all requirements are met.
- Final Certification Stage
- Assessment and Verification: A third-party evaluation conducted by IGBC to verify that the project meets the required standards.
- Certification Award: Based on the assessment, the project is awarded a certification level (Certified, Silver, Gold, or Platinum) reflecting its performance and adherence to IGBC’s green building standards.

IGBC Green Home Rating
1. Individual Homes:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Sustainable Site Selection and Planning: Ensuring the home is situated in an environmentally responsible manner.
- Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Integration: Implementing energy-saving measures and utilizing renewable energy sources.
- Water Efficiency and Conservation: Incorporating water-saving fixtures and practices.
- Use of Environmentally Friendly Materials and Resources: Choosing eco-friendly materials for construction and interior finishes.
- Indoor Environmental Quality and Health: Ensuring good indoor air quality and comfort for occupants.
- Innovation in Design and Operation: Incorporating innovative solutions for sustainability.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
2. Gated Communities:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Sustainable Site Planning: Designing community layout to minimize environmental impact.
- Energy Efficiency: Incorporating energy-efficient infrastructure and amenities.
- Water Conservation: Implementing water-saving measures for landscaping and common areas.
- Green Spaces and Landscaping: Promoting biodiversity and natural habitat within the community.
- Community Engagement: Encouraging residents to adopt sustainable practices.
- Innovation in Community Design: Implementing innovative solutions for sustainability.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
3. High-Rise Residential Buildings:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Sustainable Design and Construction: Utilizing eco-friendly building materials and construction practices.
- Energy-efficient Systems: Incorporating energy-saving systems for lighting, heating, and cooling.
- Water Management: Implementing water-saving fixtures and recycling systems.
- Indoor Air Quality: Ensuring good ventilation and using low-VOC materials.
- Waste Management: Establishing systems for waste reduction, recycling, and composting.
- Community Engagement: Encouraging residents to adopt sustainable lifestyles.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
4. Affordable Housing:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Affordability and Energy Efficiency: Ensuring homes are affordable to build and operate.
- Sustainable Design: Incorporating energy-efficient features and passive design strategies.
- Community Amenities: Providing access to public transportation, parks, and other amenities.
- Health and Safety: Ensuring homes meet safety and health standards.
- Innovation in Affordable Housing: Implementing innovative solutions to reduce construction costs and improve sustainability.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
IGBC Green Building Rating
1. Office Buildings:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Sustainable Site Development: Ensuring minimal environmental impact during construction and operation.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-saving technologies and practices.
- Water Management: Utilizing water-efficient fixtures and systems.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Providing a healthy and comfortable indoor environment for occupants.
- Sustainable Materials: Using eco-friendly materials for construction and interior finishes.
- Innovation in Design and Operation: Incorporating innovative solutions for sustainability.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
2. Retail Spaces:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Sustainable Design: Incorporating energy-efficient lighting and HVAC systems.
- Water Conservation: Implementing water-saving fixtures and practices.
- Indoor Air Quality: Ensuring good ventilation and using low-VOC materials.
- Sustainable Materials: Using eco-friendly materials for displays and furnishings.
- Green Landscaping: Creating green spaces and using native plants for landscaping.
- Innovation in Retail Sustainability: Implementing innovative strategies to reduce waste and energy consumption.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
3. Hospitality Buildings:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Sustainable Site Development: Designing for minimal environmental impact and preserving natural resources.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-saving technologies for lighting, heating, and cooling.
- Water Conservation: Installing water-saving fixtures and implementing water recycling systems.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Ensuring a healthy and comfortable indoor environment for guests.
- Sustainable Operations: Promoting waste reduction, recycling, and green cleaning practices.
- Innovation in Hospitality Sustainability: Incorporating innovative solutions to enhance sustainability and guest experience.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
4. Educational Institutions:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Sustainable Campus Planning: Designing campuses for minimal environmental impact and promoting sustainability.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-saving technologies and practices in buildings and facilities.
- Water Management: Utilizing water-saving fixtures and implementing water recycling systems.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Providing a healthy and conducive indoor environment for students and staff.
- Sustainable Curriculum: Integrating sustainability into the curriculum and promoting environmental awareness.
- Innovation in Education Sustainability: Implementing innovative solutions to enhance sustainability education and practices.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
5. Healthcare Facilities:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Sustainable Site Development: Designing healthcare facilities to minimize environmental impact and enhance healing environments.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-saving technologies and practices to reduce operational costs and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Water Conservation: Utilizing water-efficient fixtures and implementing water recycling systems to conserve water resources.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Providing a healthy indoor environment through proper ventilation, daylighting, and use of low-emission materials.
- Patient Comfort and Safety: Designing spaces to optimize patient comfort and safety while reducing healthcare-associated infections and promoting healing.
- Innovation in Healthcare Sustainability: Implementing innovative solutions to address unique challenges in healthcare facility design, operation, and maintenance.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
IGBC Green Factory Building Rating
1. Manufacturing Facilities:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Energy Efficiency in Operations: Implementing efficient processes and technologies to minimize energy consumption.
- Water Conservation and Management: Optimizing water use and implementing recycling systems to reduce water consumption.
- Sustainable Material Handling and Waste Reduction: Minimizing waste generation and promoting recycling and reuse of materials.
- Indoor Air Quality and Occupational Health: Ensuring a healthy and safe working environment for employees.
- Environmental Compliance and Impact Mitigation: Adhering to regulations and implementing measures to mitigate environmental impacts.
- Innovation in Sustainable Industrial Practices: Implementing innovative solutions to improve sustainability performance.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
2. Warehousing and Logistics Centers:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Energy Efficiency in Operations: Implementing energy-efficient lighting, heating, and cooling systems.
- Water Conservation and Management: Implementing water-saving measures and recycling systems.
- Sustainable Material Handling: Using eco-friendly materials for storage and transportation.
- Indoor Air Quality: Ensuring good ventilation and air quality for workers.
- Environmental Compliance: Adhering to environmental regulations and minimizing environmental impact.
- Innovation in Logistics Sustainability: Implementing innovative solutions to improve efficiency and sustainability in logistics operations.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
3. Cold Storage Units:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Energy Efficiency: Utilizing energy-efficient refrigeration systems and insulation to minimize energy consumption.
- Temperature Control: Maintaining precise temperature levels to ensure product integrity and minimize energy use.
- Sustainable Refrigerants: Using environmentally friendly refrigerants with low global warming potential.
- Waste Reduction: Implementing measures to reduce waste and promote recycling.
- Indoor Air Quality: Ensuring good air quality and ventilation in cold storage areas.
- Innovation in Cold Storage Sustainability: Implementing innovative technologies to improve energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
4. Processing Units:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-efficient equipment and processes to minimize energy consumption.
- Water Management: Optimizing water use and implementing recycling systems to reduce water consumption.
- Waste Reduction: Minimizing waste generation and promoting recycling and reuse of materials.
- Indoor Air Quality: Ensuring good air quality and ventilation in processing areas.
- Environmental Compliance: Adhering to environmental regulations and minimizing environmental impact.
- Innovation in Processing Sustainability: Implementing innovative solutions to improve efficiency and sustainability in processing operations.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
IGBC Net Zero Energy Building Rating
1. Residential Net Zero Energy Buildings:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Energy Efficiency Measures and Design Strategies: Incorporating energy-efficient appliances, lighting, insulation, and passive solar design.
- Integration of Renewable Energy Sources: Installing solar panels, wind turbines, or other renewable energy systems to generate electricity on-site.
- Advanced Building Automation and Control Systems: Utilizing smart thermostats, lighting controls, and energy management systems to optimize energy use.
- Energy Monitoring and Management: Implementing real-time energy monitoring systems to track energy usage and identify areas for improvement.
- Demand-Side Energy Reduction Techniques: Implementing strategies to reduce energy demand through behavior change, load shifting, and energy storage.
- Innovation in Achieving Net Zero Energy Performance: Implementing innovative technologies and design strategies to achieve net zero energy performance.
Certification Types:
- Net Zero Energy Certified: Meeting the criteria for net zero energy performance.
- Net Zero Energy Platinum: Exceeding net zero energy requirements.
- Net Zero Energy Diamond: Setting new standards for net zero energy excellence.
2. Commercial Net Zero Energy Buildings:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Energy Efficiency Measures and Design Strategies: Implementing high-performance building envelopes, efficient HVAC systems, and advanced lighting controls.
- Integration of Renewable Energy Sources: Installing solar panels, wind turbines, or other renewable energy systems to generate electricity on-site.
- Advanced Building Automation and Control Systems: Utilizing smart building technologies to optimize energy use and occupant comfort.
- Energy Monitoring and Management: Implementing real-time energy monitoring and management systems to track and optimize energy consumption.
- Demand-Side Energy Reduction Techniques: Implementing strategies such as daylighting, passive solar design, and energy-efficient appliances to reduce energy demand.
- Innovation in Achieving Net Zero Energy Performance: Implementing innovative solutions to address unique challenges and optimize building performance.
Certification Types:
- Net Zero Energy Certified: Meeting the criteria for net zero energy performance.
- Net Zero Energy Platinum: Exceeding net zero energy requirements.
- Net Zero Energy Diamond: Setting new standards for net zero energy excellence.
3. Industrial Net Zero Energy Buildings:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Energy Efficiency Measures and Design Strategies: Implementing energy-efficient equipment, processes, and building systems to minimize energy consumption.
- Integration of Renewable Energy Sources: Installing solar panels, wind turbines, or other renewable energy systems to generate electricity on-site.
- Advanced Building Automation and Control Systems: Utilizing smart technologies to optimize energy use and production processes.
- Energy Monitoring and Management: Implementing real-time energy monitoring and management systems to track and optimize energy consumption.
- Demand-Side Energy Reduction Techniques: Implementing strategies such as process optimization, waste heat recovery, and energy storage to reduce energy demand.
- Innovation in Achieving Net Zero Energy Performance: Implementing innovative solutions to improve energy efficiency and renewable energy integration.
Certification Types:
- Net Zero Energy Certified: Meeting the criteria for net zero energy performance.
- Net Zero Energy Platinum: Exceeding net zero energy requirements.
- Net Zero Energy Diamond: Setting new standards for net zero energy excellence.
IGBC Data Centres Rating
1. Data Centres:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Energy Efficiency: Use energy-efficient cooling systems, power management techniques, and energy-efficient equipment to reduce energy consumption.
- Water Conservation: Implement water-saving technologies in cooling systems and facility operations to reduce water usage.
- Sustainable Site Selection and Development: Choose sites that minimize environmental impact and promote sustainable land use practices.
- Materials and Resources: Utilize sustainable building materials, and promote recycling and waste reduction within the data centre.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Ensure good air quality and appropriate lighting conditions for operational staff.
- Innovation in Design and Operation: Incorporate advanced technologies and innovative solutions to enhance sustainability and efficiency.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
2.Server Farms:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Energy Efficiency: Optimize server and cooling efficiency, implement energy-saving measures.
- Water Conservation: Use water-efficient cooling systems and technologies.
- Sustainable Site Development: Select sites that reduce environmental impact, integrate green infrastructure.
- Materials and Resources: Use recycled and eco-friendly materials, reduce and recycle waste.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Maintain optimal conditions for servers and staff.
- Innovation: Apply cutting-edge technologies and strategies for sustainability.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
3. Telecommunications Switching Centers:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Energy Efficiency: Implement energy-efficient systems and renewable energy sources.
- Water Conservation: Utilize water-saving technologies for cooling and operations.
- Sustainable Site Development: Choose locations that support sustainable practices.
- Materials and Resources: Employ sustainable and recycled materials.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Ensure good air quality and lighting for employees.
- Innovation: Integrate innovative solutions for operational efficiency.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
Explore more about Urban and Vertical Farming in Architectural Design
IGBC Green Built Environment Rating
1. Mixed use Developments
Key Factors for Rating:
- Sustainable Site Planning: Design for minimal environmental impact, efficient land use.
- Transportation and Mobility: Promote sustainable transport options, reduce vehicular emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: Implement energy-saving measures throughout buildings and infrastructure.
- Water Management: Optimize water use, implement recycling and rainwater harvesting.
- Waste Management: Reduce waste generation, promote recycling.
- Green Infrastructure: Integrate green spaces and eco-friendly infrastructure.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Ensure healthy indoor environments across all building types.
- Community Development: Provide community facilities and enhance social well-being.
- Innovation: Apply innovative design and operational strategies for sustainability.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
2. Urban Redevelopment Projects:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Sustainable Site Planning: Design for minimal environmental impact, efficient land use.
- Transportation and Mobility: Promote sustainable transport options, reduce vehicular emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: Implement energy-saving measures throughout buildings and infrastructure.
- Water Management: Optimize water use, implement recycling and rainwater harvesting.
- Waste Management: Reduce waste generation, promote recycling.
- Green Infrastructure: Integrate green spaces and eco-friendly infrastructure.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Ensure healthy indoor environments across all building types.
- Community Development: Provide community facilities and enhance social well-being.
- Innovation: Apply innovative design and operational strategies for sustainability.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
3. Eco-Cities and Townships:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Sustainable Site Planning: Design the city/township to minimize environmental impact.
- Transportation and Mobility: Plan for sustainable transport systems, reduce emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: Implement city-wide energy-saving measures and renewable energy projects.
- Water Management: Plan for efficient water use, recycling, and harvesting at a city level.
- Waste Management: Implement comprehensive waste management systems.
- Green Infrastructure: Design extensive green spaces, parks, and eco-friendly infrastructure.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Ensure healthy living and working environments.
- Community Development: Foster strong community engagement and facilities.
- Innovation: Integrate innovative technologies and design for sustainability.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
4. Special Economic Zones (SEZs):
Key Factors for Rating:
- Sustainable Site Planning: Develop SEZs with minimal environmental impact.
- Transportation and Mobility: Ensure sustainable transport solutions within SEZs.
- Energy Efficiency: Use energy-efficient systems across industrial and commercial areas.
- Water Management: Efficient use of water resources, recycling, and conservation.
- Waste Management: Promote waste reduction, recycling, and proper disposal.
- Green Infrastructure: Incorporate green spaces and sustainable infrastructure.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Ensure healthy environments in all SEZ facilities.
- Community Development: Provide amenities and improve the quality of life for workers.
- Innovation: Implement innovative practices for SEZ development and operation
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
5. Industrial Parks:
Key Factors for Rating:
- Sustainable Site Planning: Develop parks with low environmental impact and efficient land use.
- Transportation and Mobility: Facilitate sustainable transport options for goods and employees.
- Energy Efficiency: Implement energy-saving technologies and processes.
- Water Management: Ensure efficient water use and waste-water recycling.
- Waste Management: Promote recycling, waste reduction, and proper waste management.
- Green Infrastructure: Incorporate green belts, landscaping, and eco-friendly infrastructure.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Maintain good air quality and conditions in work environments.
- Community Development: Provide facilities and services for employees and surrounding communities.
- Innovation: Apply innovative solutions in industrial processes and infrastructure.
Certification Types:
- Certified: 40-49 points – Best Practices
- Silver: 50-59 points – Outstanding Performance
- Gold: 60-74 points -National Excellence
- Platinum: 75-100 points -Global Leadership
Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment (GRIHA)
The Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment (GRIHA) was developed by The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) and the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, Government of India. GRIHA is tailored for the residential sector, emphasizing resource efficiency and minimizing environmental impact. The GRIHA certification evaluates projects based on site planning, water management, energy efficiency, and indoor environmental quality, ensuring that residential buildings contribute positively to the environment while providing comfortable living spaces.
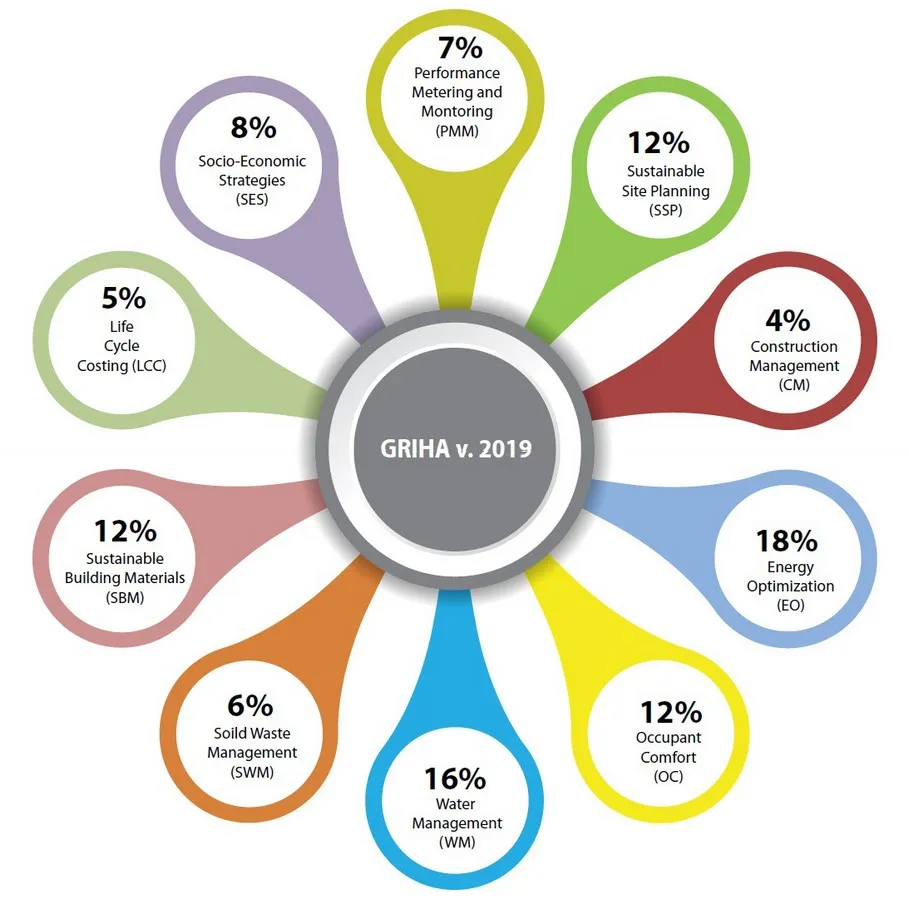
Types of Residential Buildings Covered
- Individual Homes: Standalone houses and villas.
- Apartment Buildings: Multi-family residential buildings.
- Large Residential Complexes: Integrated townships and large housing societies.
Focus Areas
- Sustainable Site Planning: Ensuring minimal environmental impact, preserving natural landscapes, and optimizing land use.
- Water Efficiency: Implementing rainwater harvesting systems, efficient plumbing fixtures, and water recycling.
- Energy Efficiency: Utilizing renewable energy sources like solar power, optimizing building orientation for natural lighting, and installing energy-efficient appliances.
- Material Selection: Promoting the use of eco-friendly, recycled, and locally sourced materials in construction.
- Waste Management: Encouraging waste segregation, recycling, and the reuse of construction and operational waste.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Ensuring good air quality through proper ventilation, using low-VOC materials, and maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures.
- Health and Well-being: Enhancing the overall living environment for occupants, promoting physical and mental well-being.
Certification Process
- Preliminary Evaluation: Initial assessment of the project’s sustainability goals and design plans. Projects must register with GRIHA and submit initial documentation.
- Design and Construction Phase: During this phase, detailed documentation must be maintained, demonstrating compliance with GRIHA criteria. This includes reports on energy and water calculations, material usage, and waste management plans.
- Site Visits and Reviews: GRIHA representatives conduct site visits to verify the implementation of green practices. This includes inspections during construction and post-completion.
- Final Assessment and Certification: After thorough evaluation and third-party verification, projects are awarded GRIHA certification based on their performance. The certification levels include One Star to Five Stars, depending on the extent of sustainability measures implemented.
U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC)
The U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) promotes sustainability through the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) certification. LEED for Homes is specifically for residential projects, ensuring they meet strict environmental and sustainability standards. This certification applies to various types of residential buildings, with criteria focusing on sustainable site development, water efficiency, energy use, and indoor air quality. LEED for Homes helps create energy-efficient and environmentally friendly residences.
Types of Residential Building Covered:
- Single-family Homes: Encompasses standalone residences, including detached houses and villas.
- Multi-family Homes: Includes apartment buildings, condominiums, townhouses, and other multi-unit residential complexes.
- Mixed-use Residential Buildings: Covers structures that combine residential and commercial spaces, promoting sustainable living in urban settings.
Focus Areas:
- Site Selection and Planning: Prioritizes sustainable site development, encouraging compact, walkable communities with access to public transportation and amenities.
- Water Efficiency: Advocates for water-saving fixtures and appliances, rainwater harvesting systems, and greywater reuse to minimize water consumption and preserve local water resources.
- Energy Efficiency: Emphasizes energy-efficient building design, including proper insulation, high-performance windows, and energy-efficient appliances, along with the integration of renewable energy sources like solar power.
- Materials and Resources: Promotes the use of environmentally preferable materials, such as recycled content, rapidly renewable resources, and locally sourced materials, while minimizing construction waste through recycling and reuse practices.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Ensures healthy indoor environments through measures such as ventilation systems, low-emitting materials, and ample natural daylighting, enhancing occupant comfort and well-being.
- Innovation and Design Process: Encourages innovative design strategies, advanced technologies, and sustainable building practices, fostering continuous improvement and environmental stewardship throughout the design and construction process.
Certification Process:
- Pre-certification Stage: Project teams register their intent to pursue certification and develop a sustainability plan aligned with USGBC’s rating system requirements.
- Design and Construction Stage: Project teams implement sustainable design and construction practices, document compliance with USGBC standards, and submit documentation for review.
- Final Certification Stage: USGBC conducts a comprehensive review of project documentation and conducts on-site inspections to verify compliance with certification criteria. Upon successful evaluation, the project is awarded one of the certification levels: Certified, Silver, Gold, or Platinum, based on the total points earned across various sustainability categories.
WELL Building Standard
The WELL Building Standard, established by the International WELL Building Institute (IWBI), focuses on enhancing health and well-being through building design and operation. WELL certification for residential buildings applies to multi-family buildings and mixed-use developments, emphasizing occupant health. Key areas covered by WELL include air quality, water quality, nourishment, light, fitness, comfort, and mind. WELL-certified buildings offer healthier living environments that support their occupants’ well-being.
Types of Residential Buildings Covered:
- Single-family Homes: Includes detached houses, cottages, and villas designed for individual occupancy.
- Multi-family Homes: Encompasses apartment buildings, condominiums, and townhouses with multiple dwelling units.
- Mixed-use Residential Buildings: Applies to buildings that combine residential units with commercial or retail spaces.
Focus Areas:
- Air: Ensuring clean indoor air quality through ventilation and filtration systems to minimize pollutants and improve respiratory health.
- Water: Providing access to clean and safe drinking water, as well as promoting hydration through innovative design features like hydration stations and water quality monitoring.
- Nourishment: Encouraging healthy eating habits by offering nutritious food options, promoting mindful eating practices, and supporting access to fresh and healthy food choices.
- Light: Optimizing natural and artificial lighting to support circadian rhythms, enhance productivity, and reduce eye strain and fatigue.
- Fitness: Promoting physical activity and movement through active design elements such as fitness centers, walking paths, and ergonomic workstations.
- Comfort: Creating comfortable indoor environments by regulating temperature, humidity, and acoustics to enhance occupant satisfaction and well-being.
- Mind: Supporting mental health and stress reduction through design features that promote relaxation, mindfulness, and social interaction, as well as providing access to mental health resources and support services.
Certification Process:
- Pre-certification Stage: Project teams register their intent to pursue WELL certification, conduct a preliminary assessment of project feasibility, and engage with a WELL Accredited Professional (AP) to develop a customized plan.
- Design and Construction Stage: Project teams implement design and construction strategies aligned with WELL requirements, document compliance, and submit documentation for review.
- Final Certification Stage: The International WELL Building Institute (IWBI) conducts a thorough review of project documentation and performance data, including on-site assessments and performance testing, to verify compliance with WELL standards. Upon successful evaluation, the project is awarded WELL certification at one of the certification levels: Silver, Gold, or Platinum, based on the total points earned across various wellness categories.
Global Real Estate Sustainability Benchmark (GRESB)
The Global Real Estate Sustainability Benchmark (GRESB) assesses the sustainability performance of real estate portfolios and infrastructure projects worldwide. While primarily focused on investment portfolios, GRESB’s criteria can also apply to residential properties. GRESB evaluates aspects such as management and policy, implementation and measurement, and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. This assessment helps investors and developers understand and improve the sustainability of their residential projects.
Types of Residential Buildings Covered:
- Multi-family Residential Properties: Includes apartment buildings, condominiums, and housing complexes with multiple dwelling units.
- Mixed-use Developments: Encompasses residential buildings integrated with commercial, retail, or office spaces.
- Residential Investment Portfolios: Represents investment funds, real estate investment trusts (REITs), and institutional investors with holdings in residential properties.
Focus Areas:
- Management and Policy: Evaluates the implementation of sustainability policies, management systems, and governance practices at the property or portfolio level.
- Implementation and Measurement: Assesses the execution of sustainability initiatives, performance monitoring, and reporting processes to track environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics.
- ESG Performance: Measures the environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices of residential properties, including energy efficiency, water conservation, waste management, community engagement, and stakeholder relations.
Certification Process:
- Data Collection: Property owners or asset managers submit data and information on sustainability performance metrics through the GRESB online portal.
- Assessment and Benchmarking: GRESB assesses the submitted data based on its standardized criteria and benchmarks the performance of residential properties against industry peers.
- Scoring and Reporting: GRESB assigns scores to participating properties and portfolios, providing detailed feedback and analysis on their sustainability performance relative to market benchmarks.
- Investor Reporting: GRESB publishes annual reports and benchmarking results, enabling investors to evaluate the sustainability performance of residential investments and make informed decisions based on ESG criteria.
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI)
The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) provides a framework for sustainability reporting, helping organizations communicate their environmental, social, and economic impacts. Developers and organizations involved in residential projects can use GRI standards to report on their sustainability efforts. The framework covers economic performance, environmental impact, and social responsibility, promoting transparency and accountability. By adopting GRI standards, residential developers can demonstrate their commitment to sustainable practices and responsible development.
Types of Residential Buildings Covered:
- Single-family Homes: Includes detached houses, bungalows, and villas designed for individual occupancy.
- Multi-family Residential Buildings: Encompasses apartment complexes, townhouses, and condominiums with multiple dwelling units.
- Mixed-use Developments: Represents residential properties integrated with commercial, retail, or office spaces within the same building or complex.
Focus Areas:
- Economic Performance: Discloses financial aspects related to residential projects, including revenue, expenses, investments, and financial risks.
- Environmental Impact: Reports on the environmental footprint of residential developments, covering energy consumption, water usage, greenhouse gas emissions, and waste generation.
- Social Impact: Addresses the social aspects of residential projects, such as community engagement, labor practices, health and safety measures, and stakeholder relations.
Certification Process:
- Data Collection: Residential developers or property owners collect data on economic, environmental, and social performance indicators relevant to GRI reporting requirements.
- Reporting Framework: Utilizing the GRI Standards, residential projects disclose sustainability-related information in accordance with the GRI Reporting Principles and Reporting Guidelines.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engage with stakeholders, including residents, investors, regulators, and local communities, to gather feedback and input on sustainability initiatives and reporting practices.
- Independent Assurance: Optionally, residential projects may undergo independent assurance or verification of their sustainability reports to enhance credibility and transparency.
- Publication and Disclosure: Publish sustainability reports detailing the economic, environmental, and social performance of residential projects, making them accessible to stakeholders and the public through various channels.
Get your checklists for Green Building Regulations and Certifications

Regulations for Green Building
National Building Code (NBC) of India
The National Building Code (NBC) of India sets standards for building design and construction to ensure safety, sustainability, and efficiency. Specific sections of the NBC address green building provisions, including energy efficiency, water conservation, and the use of sustainable materials. Compliance with these standards is mandatory for new residential projects. By following the NBC, developers can ensure their residential buildings meet sustainability criteria and contribute to environmental conservation.
Green Building Provisions:
- Energy Efficiency: NBC emphasizes energy-efficient building design and construction methods to minimize energy consumption and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. It includes provisions for insulation, efficient lighting systems, and renewable energy integration.
- Water Conservation: NBC promotes water conservation measures by encouraging the use of low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and wastewater recycling technologies to reduce the demand for potable water and alleviate strain on water resources.
- Sustainable Materials: The code encourages the use of sustainable building materials, such as recycled content, locally sourced materials, and low-emission products, to minimize environmental impact and promote resource efficiency.
- Site Planning and Design: NBC advocates for sustainable site planning and design practices that minimize environmental disturbance, preserve natural habitats, and promote biodiversity. It includes guidelines for site selection, landscaping, and stormwater management.
Compliance Requirements:
- Mandatory Adherence: Compliance with NBC’s green building provisions is mandatory for all new construction projects seeking approval from local building authorities.
- Implementation Guidelines: NBC provides detailed implementation guidelines and recommendations to assist architects, engineers, and builders in incorporating green building practices into their projects effectively.
- Third-party Verification: In some cases, compliance with NBC’s green building provisions may require third-party verification or certification to ensure adherence to prescribed standards and guidelines.
Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC)
Developed by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), the Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) promotes energy efficiency in building construction. The ECBC applies to residential projects, especially those of a certain size. It sets minimum energy performance standards and outlines methods for compliance. By adhering to the ECBC, residential projects can achieve significant energy savings, reducing their overall environmental impact and operational costs.
Green Provisions:
- Minimum Energy Performance Standards: ECBC sets minimum energy performance standards for various building components and systems, including building envelope, lighting, HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), and electrical systems. These standards are based on factors such as building type, occupancy, and climate zone.
- Building Envelope Requirements: ECBC includes requirements for building envelope design and construction to enhance thermal insulation, minimize air leakage, and optimize natural lighting while reducing heat gain and loss.
- Efficient Lighting Systems: ECBC mandates the use of energy-efficient lighting systems, such as Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) and compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs), to reduce electricity consumption for lighting purposes.
- HVAC Efficiency: ECBC establishes standards for HVAC system efficiency, including equipment performance ratings, duct design, and controls, to minimize energy consumption for space heating, cooling, and ventilation.
Applicability:
ECBC applies to new construction projects, major renovation projects, and existing buildings undergoing substantial alterations or upgrades. It is applicable to various building types, including residential, commercial, institutional, and industrial buildings, across different climatic zones in India.
Compliance Criteria:
- Performance-Based Approach: ECBC adopts a performance-based approach to compliance, allowing flexibility in meeting energy efficiency requirements through alternative design strategies, technologies, and renewable energy integration.
- Compliance Verification: Compliance with ECBC is typically verified through energy modeling, simulations, and on-site inspections conducted by certified energy auditors or third-party assessors to ensure adherence to prescribed standards and guidelines.
State-Level Regulations
In addition to national regulations, there are state-level adaptations based on specific environmental and climatic conditions. For example, Maharashtra has its own Green Building Guidelines, while Delhi has a Green Building Policy. These state-level regulations offer incentives for compliance and impose penalties for non-compliance, encouraging adherence to green building practices. Understanding and complying with both national and state regulations ensures residential projects meet all necessary sustainability criteria.
Examples:
- Maharashtra Green Building Guidelines: Maharashtra, with its diverse climate and urbanization challenges, has developed its own set of green building guidelines to promote sustainable construction practices. These guidelines prioritize energy efficiency, water conservation, and waste management while accommodating the state’s unique environmental and socio-economic contexts.
- Delhi Green Building Policy: Delhi, as the capital territory and a densely populated urban center, faces distinct environmental and infrastructure challenges. The Delhi government has implemented a Green Building Policy to incentivize the adoption of green building practices through regulatory frameworks, financial incentives, and capacity-building initiatives tailored to the city’s specific needs and priorities.
Benefits of Green Building Certification
Green building certification offers numerous benefits. Environmentally, it reduces the carbon footprint and conserves natural resources. Economically, certified buildings typically have lower utility bills and increased property value. From a health perspective, green buildings provide improved indoor air quality and better living conditions. Additionally, green certification offers market differentiation, attracting environmentally conscious buyers and enhancing the project’s marketability.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the benefits, implementing green building practices can pose challenges, including costs, awareness, and regulatory hurdles. However, the future of green building is promising, with advances in technology, evolving certification standards, and increased government incentives and policies driving growth. Addressing these challenges will be crucial in promoting widespread adoption of sustainable practices in residential construction.
Green building certifications play a crucial role in promoting sustainable residential construction. They offer numerous benefits, including environmental conservation, economic savings, and enhanced occupant health. By pursuing these certifications, developers and homeowners can contribute to a sustainable future and meet the growing demand for eco-friendly homes.
Explore more about Sports Pitches and Courts : Comparative Size and Analysis




