A Bill of Quantities (BOQ) is a vital document in the construction industry, meticulously listing all the materials, labor, and equipment necessary for completing a construction project. It breaks down every aspect of the project, covering structural elements, finishes, and mechanical and electrical systems in detail. For each item of work, the BOQ provides precise quantities, units of measurement, rates, and total amounts, enabling contractors to accurately estimate project costs and submit competitive bids.
BOQ also plays a crucial role in the tendering process, which involves awarding contracts for construction projects. It is included in the tender documentation alongside other important documents such as the general and special conditions of the contract, technical specifications, and the schedule of finishes. By providing insights into the project scope and requirements, BOQ facilitates accurate cost estimation and streamlines the tendering process, aiding in contractor selection and contract award.
Throughout the construction lifecycle, BOQ remains a cornerstone reference document. It guides procurement activities, assists in project management, and ensures effective cost control. By offering clarity and transparency regarding project requirements and costs, BOQ significantly contributes to the successful execution and completion of construction projects, helping to keep projects on track and within budget.
What are the key components of a BOQ?
- Item Description: This entails a clear and concise definition of the scope of work, outlining the proposed system and methodology to be employed.
- Quantity: This represents the total amount or volume of a particular type of work required for the project.
- Unit: The unit of measurement assigned to quantify the work, which varies based on the nature of the task, including options such as cubic meters (CUM), square meters or square feet, running meters, counts, etc.
- Rate per unit: The predetermined cost per unit of measurement, often derived from established reference documents like the Delhi Schedule of Rates (DSR), providing a benchmark for common construction activities.
- Amount: Calculated by multiplying the overall quantity by the rate per unit, yielding the total cost for the specific item or scope of work.
See also article on – Construction cost calculation – excel calculator
What is the format of a BOQ?
Standard BOQ format consists of the item of work, unit, quantity, rate, and amount.
Get your Construction Cost Calculator from us

How is BOQ prepared?
- Scope Identification: The first step is to identify the scope of work for the construction project. This involves thoroughly reviewing the project plans, specifications, and any other relevant documentation to understand the full extent of the work to be performed.
- Item Description: Each item of work included in the BOQ should be clearly described. This description should provide a brief overview of the work scope, including the system and methodology proposed for its execution.
- Quantity Calculation: Quantities for each item of work are determined through a process known as quantity takeoff. This involves extracting measurements from the project drawings, which can be done manually or with the assistance of software tools. The quantities should be accurate and reflect the actual requirements for completing the work.
- Unit of Measurement: For each item of work, the appropriate unit of measurement is specified. This could include units such as cubic meters (CUM), square meters or square feet, running meters, counts, etc. The unit of measurement should align with the nature of the work being quantified.
- Rate Analysis: Once quantities have been determined, unit rates are established for each item of work. This involves conducting a rate analysis to determine the cost of materials, labor, and equipment required to complete the work. Reference documents such as schedules of rates or historical cost data may be used to establish unit rates.
- Amount Calculation: The amount for each item of work is calculated by multiplying the quantity by the unit rate. This provides the total cost for that particular scope of work.
- Formatting and Presentation: The BOQ is then formatted and presented in a standardized layout, typically consisting of columns for item description, quantity, unit, rate per unit, and total amount. This ensures clarity and ease of understanding for all stakeholders involved in the project.
- Review and Verification: Finally, the completed BOQ should be thoroughly reviewed and verified for accuracy and completeness. Any discrepancies or inconsistencies should be addressed before finalizing the document.
Also explore on Cost of Construction: Estimating Methods
What are the different types of BOQ?
There can be 3 broad categories of BOQ.
- Bill of quantities – It provides a comprehensive list of all the materials, labor, and equipment required and evaluates the project cost. It helps in understanding the scope of work in terms of quantities, units, and rates for each item, and also helps in calculating the accurate cost estimation, streamline efficient tendering process and to compare the bids from various contractors.
- Bill of materials – It mainly focuses and provides clarity on the materials and supplies needed for the construction project. It includes detailed specifications and quantities for each material required and is primarily used for procurement purposes, which helps in sourcing and purchasing materials from suppliers.
- Bill of labor – It lists out types of labor, their qualification, and the estimates hours and days are required for each task to execute the construction project. It helps in estimating labor costs, and helps in planning and scheduling construction activities.
What are the different elements or trades involved in BOQ for construction & tendering?
The different elements or trades involved in BOQ for construction are as follows:
- Substructure Works: It involves the construction of the foundation and supporting structures below ground level, including tasks such as excavation, footing, piling, and subflooring.
- Superstructure Works: This comprises the main framework and load-bearing structures of a building above ground level, incorporating columns, beams, slabs, walls, and other structural elements.
- Finishing Works: These focus on enhancing the aesthetics and functionality of interior and exterior spaces, encompassing plastering, painting, tiling, flooring, cladding, and decorative elements.
- Podium / Car Parking Works: It Involves in the construction of elevated platforms or levels to accommodate vehicles, this includes ramps, decks, parking bays, and associated structural elements.
- Waterproofing Works: It ensure protection against water infiltration and damage in buildings and structures through membrane installation, sealing, and drainage systems.
- Expansion Joint Works: It provides flexibility to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction in structures, this involves the installation of expansion joint systems in floors, walls, and other building elements.
- Post Tensioning Works: These enhance the structural integrity and load-bearing capacity of concrete elements through the installation of post-tensioning tendons and stressing operations.
- Electrical Works: It involves the installation of electrical systems and components to provide power and lighting, this includes wiring, distribution panels, fixtures, switches, and outlets.
- Plumbing Works: It is mainly focused in the installation of plumbing systems for water supply, drainage, and sanitation, this includes piping, fixtures, fittings, valves, and drainage networks.
- Mechanical Works: This is primarily about the installation of mechanical systems for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC), as well as other mechanical equipment, this includes ductwork, HVAC units, boilers, chillers, pumps, and associated controls.
- Fire Fighting Works: It focuses on the installation of fire suppression systems and equipment to ensure fire safety, this includes sprinkler systems, fire alarms, extinguishers, hydrants, and fireproofing materials.
- Hardscape Works: This includes the construction of non-living, durable features in outdoor spaces, such as pavements, pathways, retaining walls, fences, and outdoor structures.
- Softscape Works: This includes the installation of living elements in outdoor landscapes, including planting, landscaping, turfing, irrigation systems, and garden features.
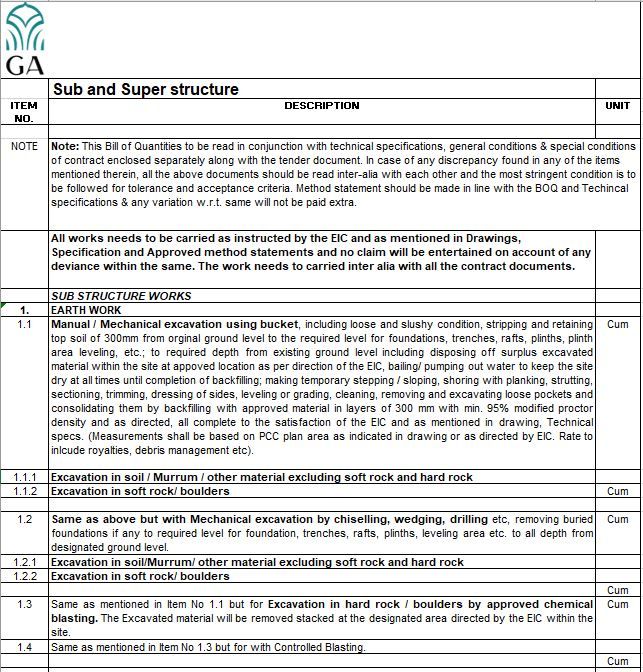
Based on the tendering strategy or scope few of the above scopes can be floated together as part of a package. Usually, it is seen, that Civil works, MEPF works, Infra works, and Landscape works are floated as separate packages.
What are the benefits of BOQ for Construction & Tendering?
The following are the benefits of BOQ:
- Scope Definition: BOQ defines the scope of work for the project, outlining the specific tasks and components involved in construction.
- Cost Estimation: It helps in estimating the cost of the project by providing quantities, units, and rates for each item of work. This allows for accurate budgeting and cost forecasting.
- Tendering Process: BOQ forms an essential part of the tender documentation, helping in the tendering process by providing contractors with a clear understanding of the project scope and requirements.
- Contractual Clarity: It establishes a clear basis for the contract between the client and the contractor, ensuring that both parties have a common understanding of the work to be performed and the associated costs.
- Comparison of Bids: Contractors can use BOQs to prepare and submit bids for the project. Clients can then compare bids from various contractors based on the quantities, rates, and overall cost provided in the BOQ.
- Procurement Guidance: BOQ assists in the procurement process by specifying the materials, quantities, and quality standards required for the project. This helps in sourcing and purchasing materials from suppliers.
- Project Management: Once the project is underway, BOQ serves as a reference document for monitoring progress and managing resources, ensuring that the work is carried out according to the agreed-upon specifications and budget.
How to takeoff quantity for BOQ for construction & tendering?
- Manual Quantity Take-Off – This is the traditional type of quantity takeoff, wherein an estimator reviews drawings or blueprints to take out quantities physically for a trade or execution scope. As such this is a time-consuming process and subject to human errors. It is also largely dependent on the estimator’s experience and knowledge of different materials.
- Digital Quantity Take-off – This kind of take-off from CAD applications is relatively new in the construction industry. Digital take-offs are superior to manual take-offs due to the scale and thoroughness digital tools provide. Digital take-off tools are developing rapidly, and we expect manual quantity take-off to be replaced very shortly.
Explore on Pre-Design Phase in Construction & Real Estate Projects
Hope you have found value reading the article. We would like to hear your comments or feedback at mail@greenarchworld.com.
For more articles on architecture and construction related topics, click here




